Understanding Electrical Circuits
- Nov 4, 2024
- 2 min read

by Dr. Bryan R Miranda
Electrical circuits are the backbone of modern technology, powering everything from household appliances to complex industrial systems. This blog will provide a clear and concise overview of electrical circuits, their types, and how they are used in everyday life. Whether you're a student or just curious about how electricity works, this guide will help you understand the basics.
What is an Electrical Circuit?
An electrical circuit is a path that allows electric current to flow. This flow of electricity is essential for powering any device or machine. A simple circuit consists of three main components:
Power Source: Provides the electricity (like a battery or power outlet).
Conductive Path: Usually wires that carry the electricity from the power source to the device.
Load: The device or component that uses the electricity to perform work, such as a light bulb or motor.
Types of Electrical Circuits
Understanding the different types of circuits is key to knowing how various devices operate. There are two primary types of circuits:
1. Series Circuits
In a series circuit, components are connected end-to-end in a single path. Here, the electric current flows through each component one after the other. If one component fails, the entire circuit is broken.
Uses:
Christmas Lights: Older string lights are a common example. If one bulb goes out, the whole string stops working.
Flashlights: Many simple flashlights use series circuits.
Advantages:
Easy to set up and require fewer wires.
Disadvantages:
If one part fails, the entire circuit stops working.
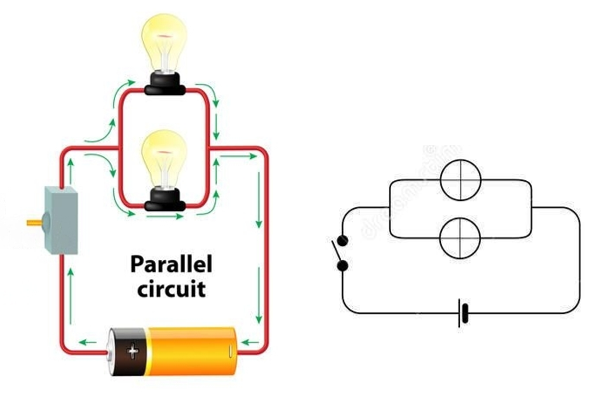
2. Parallel Circuits
In a parallel circuit, components are connected across common points, creating multiple paths for the current. If one path fails, the current can still flow through other paths.
Uses:
Home Wiring: Most houses are wired in parallel so that if one light goes out, the others remain on.
Computers and Electronic Devices: Parallel circuits are essential in complex electronics for reliable performance.
Advantages:
More reliable because if one path fails, the others continue to work.
Devices can operate independently of each other.
Disadvantages:
More complex to set up and require more wiring.
Electrical circuits are vital to powering the world around us. Understanding the difference between series and parallel circuits is crucial for grasping how electricity works in various devices. By knowing the basics, you can better appreciate the technology you use every day and even troubleshoot simple electrical issues. Whether it’s the lights in your home or the device you’re using to read this blog, circuits make it all possible.


Comments